About Diabetic Retinopathy
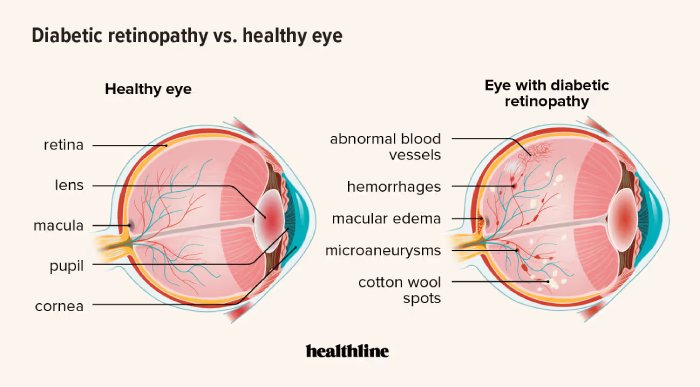
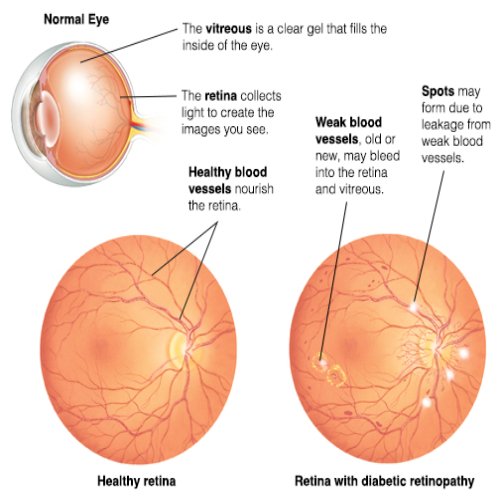
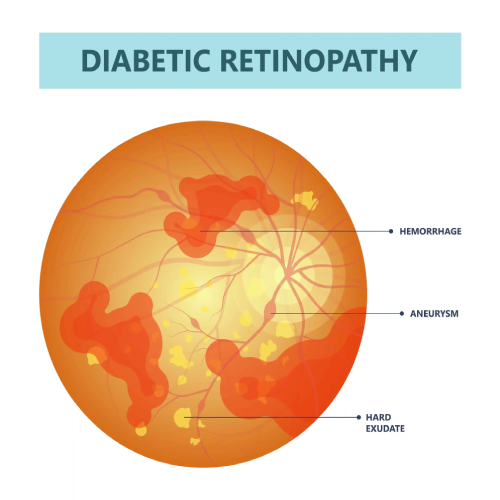
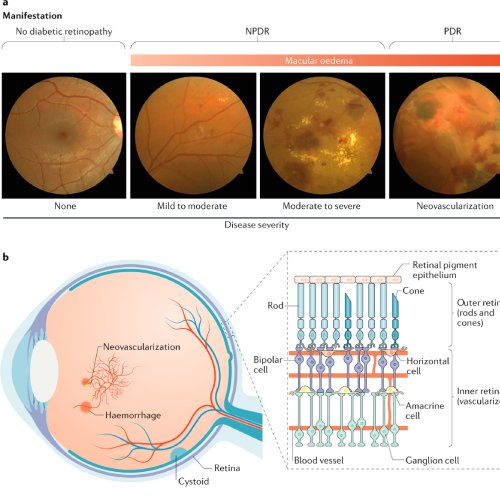
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can affect people with diabetes. It occurs when high blood sugar levels cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, these damaged vessels can leak blood or fluid, leading to swelling of the retinal tissue, blurred vision, or even permanent vision loss if untreated.
Symptoms of Diabetic retinopathy
- Blurred vision
- Fluctuating vision
- Floaters
- Impaired color vision
- Dark or empty spots in the vision
- Sudden vision loss

Causes of Diabetic retinopathy
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Persistent high glucose levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, causing them to leak fluid or bleed.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension adds extra strain on the already weakened blood vessels in the eyes, exacerbating the damage.
Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
Poor Diabetes Control: Inadequate management of blood sugar levels increases the risk.
High Cholesterol: High cholesterol can contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in the blood vessels, leading to retinal damage.
Other Medical Conditions: Conditions like kidney disease or high cholesterol can increase the likelihood of developing retinopathy.
Our Diabetic retinopathy Treatment Options
Laser Photocoagulation: This procedure uses a laser to seal leaking blood vessels and reduce abnormal blood vessel growth, helping to prevent further retinal damage
Intravitreal Injections: Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) medications are injected into the eye to block the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels and reduce fluid leakage
Vitrectomy: In advanced cases, surgery is performed to remove the vitreous gel from the eye and repair or remove damaged blood vessels and scar tissue
Corticosteroid Injections or Implants: These are used to reduce inflammation and can be effective in treating macular edema associated with diabetic retinopathy
When You Need
Treatment Diabetic retinopathy
- Preventing Vision Loss: Diabetic retinopathy, if left untreated, can lead to severe vision problems, including partial or complete blindness. Early treatment can help preserve vision and prevent the condition from worsening.
- Slowing Disease Progression: Treatments like laser therapy, injections, or surgery can slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. This is crucial because the disease tends to worsen over time, especially without intervention.
- Reducing Swelling and Fluid Buildup: Diabetic retinopathy often causes fluid and blood leakage into the retina. Treatments like anti-VEGF injections help reduce swelling (macular edema) and prevent damage to the retina.
Frequently Asked Questions
Anyone with diabetes (Type 1 or Type 2) is at risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. The longer a person has diabetes and the less controlled their blood sugar levels are, the higher their risk. Other factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and pregnancy.
An eye doctor (ophthalmologist) diagnoses diabetic retinopathy during a comprehensive dilated eye exam. The doctor will examine the retina for signs of damage, blood vessel changes, and any swelling. Additional tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography may be used.
Yes, it can be prevented or its progression slowed with proper management of diabetes. Maintaining good control of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels, along with regular eye exams, can help prevent or delay diabetic retinopathy.
Yes, if left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can cause severe vision loss and blindness. Early detection and treatment can significantly reduce this risk.
24 / 7 HOURS SERVICE
