About Ocular Trauma
Ocular trauma refers to any injury to the eye or the surrounding structures, such as the eyelids, orbit, or optic nerve. These injuries can range from minor, such as superficial scratches, to severe, such as globe rupture or optic nerve damage, which can result in vision loss or even blindness if not treated promptly.
Symptoms of Ocular Trauma
- Eye Pain
- Blurred Vision
- Loss of Vision
- Double Vision
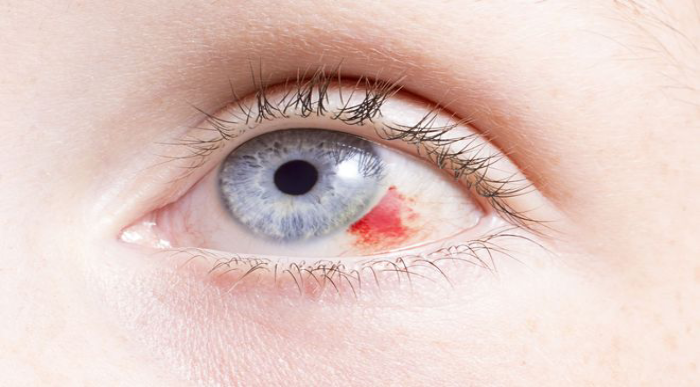
- Blood in the Eye (Hyphema)
- Redness
- Floaters or Flashes
- Light Sensitivity (Photophobia)
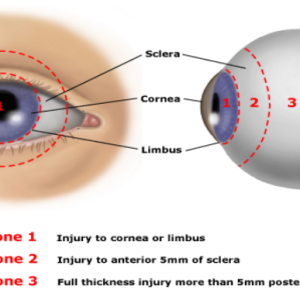
Causes of Ocular Trauma
1. Blunt Trauma
- Sports Injuries: Common in contact sports like boxing, football, basketball, and soccer, where blows to the eye can occur.
- Falls or Accidents: Falls at home, work, or during recreational activities can lead to direct impact on the eye.
- Car Accidents: Airbags or debris during accidents can cause blunt trauma to the eye.
- Assault: Physical altercations or accidents involving punches or strikes to the eye.
2. Penetrating or Perforating Injuries
- Sharp Objects: Injuries caused by sharp objects like knives, scissors, nails, or broken glass can penetrate the eye, causing severe damage.
- Projectiles: Small flying objects, such as wood or metal shavings, or objects from tools like drills or hammers, can cause perforating injuries.
- Explosions: Shrapnel from explosions or fireworks can penetrate the eye and surrounding areas.
3. Foreign Bodies
- Dust, Sand, and Debris: Small particles can enter the eye, causing irritation or scratches to the cornea.
- Metal or Wood Splinters: Often found in industrial settings or DIY projects, these materials can lodge in the eye.
Our Ocular Trauma Treatment Options
1. First Aid and Immediate Care
- Flush the Eye: For chemical burns or foreign bodies, flushing the eye with clean water or saline solution can help remove harmful substances or debris.
- Cover the Eye: For penetrating or perforating injuries, it’s important to cover the eye with a protective shield or clean cloth and avoid putting pressure on it.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the area around the eye can help reduce swelling from blunt trauma or bruising.
2. Medical Treatment for Specific Injuries
- Foreign Body Removal: A doctor will carefully remove foreign objects from the eye using special instruments. In some cases, anesthesia may be required for the procedure.
- Corneal Abrasion Treatment: Small scratches or abrasions on the cornea are treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointments to prevent infection, along with pain-relieving eye drops.
- Chemical Burn Treatment: Immediate irrigation of the eye to flush out the chemicals, followed by medication like steroids or pain relief to control inflammation. Severe cases may require surgery.
- Hyphema Management (Blood in the Eye): Elevating the head, using eye drops, and limiting physical activity are common treatments for hyphema. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove blood clots.
When You Need
Treatment Ocular Trauma
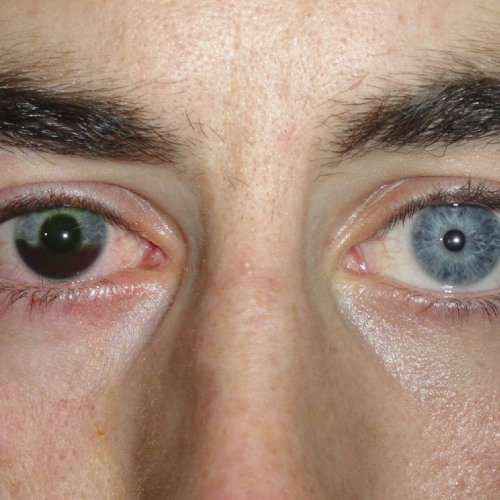

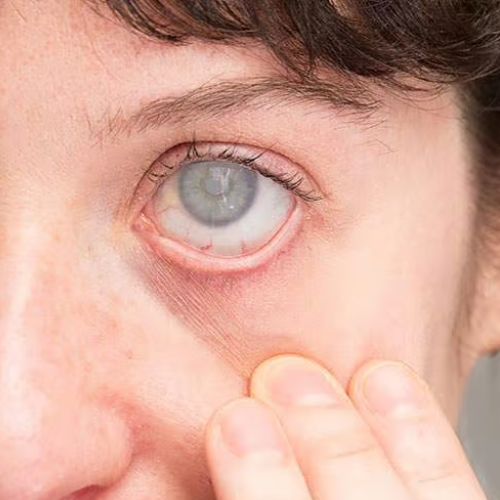
1. Prevent Permanent Vision Loss
- Ocular trauma can cause damage to vital parts of the eye, such as the retina, cornea, or optic nerve. Without treatment, even minor injuries can worsen over time, leading to irreversible vision loss or blindness.
2. Reduce Risk of Infection
- Eye injuries, especially those involving cuts or foreign objects, can expose the eye to bacteria, leading to infections like endophthalmitis or corneal ulcers. Timely treatment with antibiotics can prevent these serious infections, which could otherwise cause long-term damage.
3. Control Pain and Inflammation
- Eye injuries can be extremely painful, and without treatment, swelling and inflammation can worsen, increasing discomfort. Medical intervention helps manage pain, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Common causes include blunt force trauma (from sports or falls), penetrating injuries (sharp objects or projectiles), chemical burns (household cleaners or industrial chemicals), thermal burns (hot liquids or explosions), and radiation exposure (UV rays or welding arcs).
For minor injuries, you can rinse your eye with clean water or saline and apply a cold compress to reduce swelling. For severe injuries, avoid rubbing the eye, do not remove any embedded objects, and seek emergency medical care immediately.
Yes, untreated ocular trauma can result in permanent vision loss or blindness, especially if the injury affects critical structures like the retina, optic nerve, or cornea. Prompt medical treatment is crucial to preserve vision.
Avoid rubbing the injured eye, applying pressure to it, or attempting to remove objects stuck in the eye. Also, refrain from using eye drops unless recommended by a doctor and avoid exposing the eye to harsh light.
24 / 7 HOURS SERVICE
